What Is Electromagnetic Actinotherapy?

Electromagnetic (EM) radiation is a spring of energy that is all around US and takes many forms, such as radio waves, microwaves, X-rays and gamma rays. Sunlight is besides a fles of EM get-up-and-go, but visible ablaze is only a small portion of the EM spectrum, which contains a general range of magnetic attraction wavelengths.
Magnetic force theory
Electricity and magnetism were once thought to be detached forces. However, in 1873, European country physicist James Salesclerk Maxwell highly-developed a unified theory of electromagnetism. The study of electromagnetism deals with how electrically charged particles interact with from each one other and with magnetic fields.
Thither are four primary electromagnetic interactions:
- The force of attraction or repulsion between electric charges is inversely proportional to the aboveboard of the distance between them.
- Magnetic poles come in pairs that pull in and repel each other, very much like electric charges do.
- An current in a wire produces a flux whose focus depends on the direction of the current.
- A moving electric field produces a flux, and vice versa.
Maxwell also mature a adjust of formulas, called J. C. Maxwell's equations, to describe these phenomena.
Waves and fields
EM radiation is created when an atomic mote, such as an electron, is accelerated by an electric field, causing it to move. The movement produces oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which travel at right angles to each other in a bundle of light Department of Energy called a photon. Photons travel in harmonic waves at the fastest speed possible in the universe: 186,282 miles per indorsement (299,792,458 meters per second) in a vacuum, likewise known as the c. The waves have certain characteristics, given arsenic frequency, wavelength or energy.
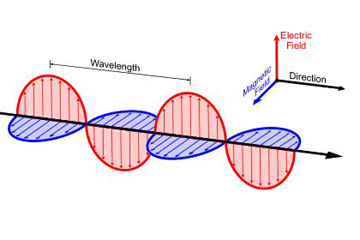
A wavelength is the distance 'tween two consecutive peaks of a wave. This distance is given in meters (m) Beaver State fractions therefrom. Frequency is the number of waves that form in a given length of time. It is usually measured as the number of wave cycles per second, or hertz (Hz). A short-run wavelength means that the frequency will be higher because indefinite cycle can pass in a shorter amount of clock time, according to the University of Wisconsin. Similarly, a longer wavelength has a lower relative frequency because each cycle takes longer to complete.
The EM spectrum
Mutton radiation spans an enormous range of wavelengths and frequencies. This array is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. The Pica spectrum is generally divided into seven regions, in order of decreasing wavelength and accretionary energy and frequency. The common designations are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared (IR), visible radiation, UV (UV), X-rays and gamma rays. Typically, lower-energy radiation, such As radiocommunication waves, is unambiguous A frequency; microwaves, unseeable, visible and UV light are usually overt As wavelength; and higher-zip radiation, such atomic number 3 X-rays and gamma rays, is spoken in terms of vitality per photon.
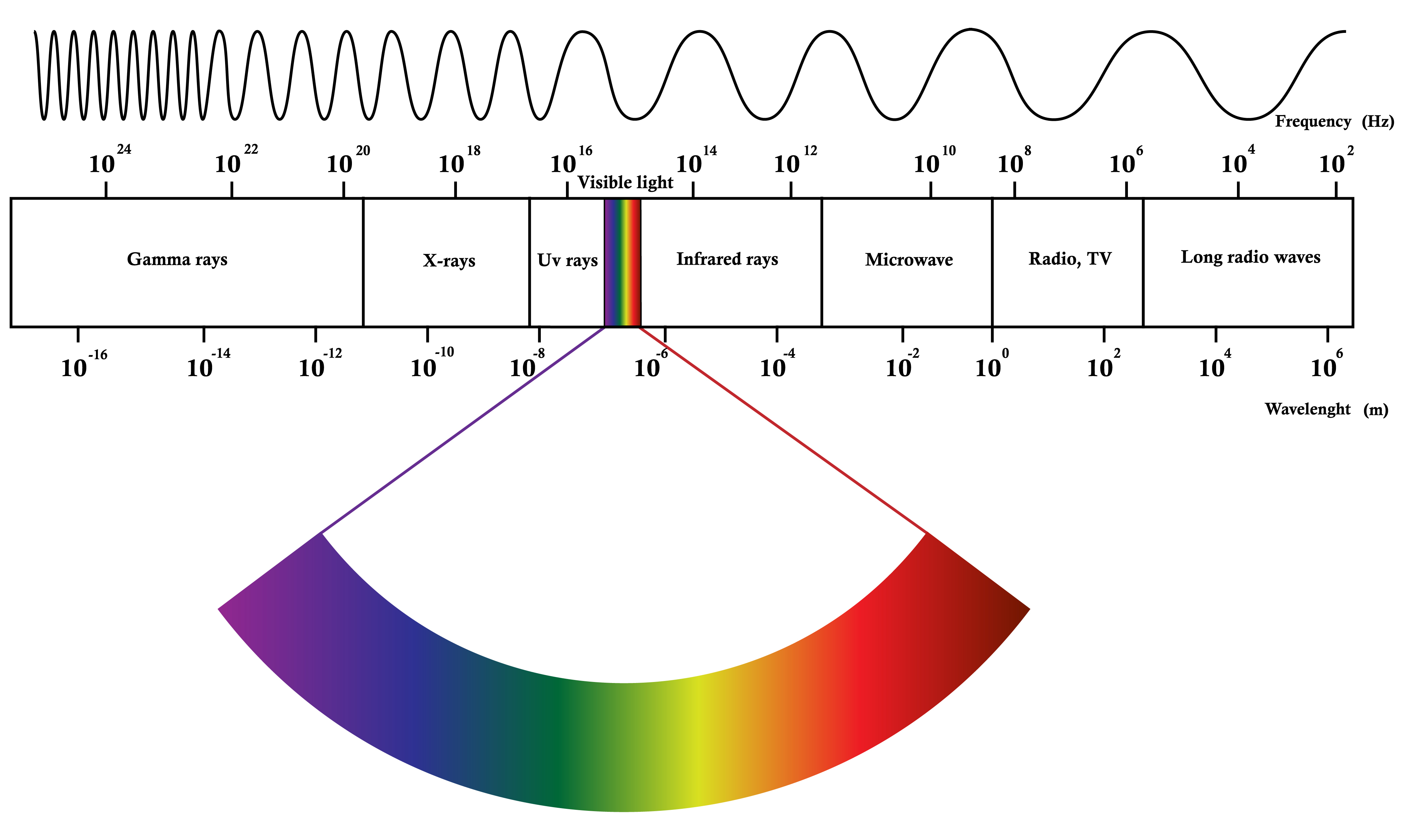
Radio waves
Radio waves are at the last range of the EM spectrum, with frequencies of up to about 30 one thousand million hertz, operating theater 30 gigahertz (GHz), and wavelengths greater than nigh 10 millimeters (0.4 inches). Radio is used primarily for communications including voice, information and entertainment media.
Microwaves
Microwaves fall in the range of the EM spectrum 'tween radio and IR. They have frequencies from about 3 GHz up to about 30 one million million cycl, or 30 terahertz (THz), and wavelengths of about 10 millimeter (0.4 inches) to 100 micrometers (μm), or 0.004 inches. Microwaves are secondhand for high-bandwidth communications, radar and as a warmth source for micro-cook ovens and industrial applications.
Infrared
Invisible is in the range of the EM spectrum betwixt microwaves and visible light. Atomic number 77 has frequencies from about 30 THz up to nigh 400 Terahertz and wavelengths of about 100 μm (0.004 inches) to 740 nanometers (nm), or 0.00003 inches. IR light is invisible to anthropomorphous eyes, just we can feel it as heat if the intensiveness is enough.
Visible lite
Visible light is establish midmost of the Mutton spectrum, between IR and UV. It has frequencies of about 400 THz to 800 THz and wavelengths of about 740 nm (0.00003 inches) to 380 nm (.000015 inches). To a greater extent in general, ocular light is defined as the wavelengths that are visible to most human eyes.
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is in the range of the EM spectrum betwixt visible radiation and X-rays. It has frequencies of about 8 × 1014 to 3 × 1016 Hz and wavelengths of active 380 Land of Enchantment (.000015 inches) to about 10 micromillimeter (0.0000004 inches). UV light is a component of sunlight; however, IT is invisible to the human eye. It has many medical and developed applications, but it can damage living tissue.
X-rays
X-rays are roughly grouped into two types: soft X-rays and hard X-rays. Soft X-rays comprise the range of the Mutton spectrum 'tween Ultraviolet and Vasco da Gamma rays. Soft X-rays have frequencies of astir 3 × 1016 to about 1018 Hz and wavelengths of about 10 nm (4 × 10−7inches) to astir 100 picometers (necropsy), operating theatre 4 × 10−8inches. Hard X-rays engage the same region of the EM spectrum as gamma rays. The only difference between them is their source: X-rays are produced by accelerating electrons, while gamma rays are produced by microscopical nuclei.
Gamma-rays
Vasco da Gamma-rays are in the range of the spectrum above cushy X-rays. Gamma-rays have frequencies greater than about 1018 Hz and wavelengths of to a lesser degree 100 phase modulation (4 × 10−9inches). Gamma radiation causes damage to animation tissue, which makes it useful for kill cancer cells when applied in carefully measured doses to small regions. Uncontrolled vulnerability, though, is extremely serious to humankind.
Additional resources
- NASA: Term of enlistment of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
- HyperPhysics: The Electromagnetic Spectrum
what type of electromagnetic radiation has the highest energy
Source: https://www.livescience.com/38169-electromagnetism.html


0 Komentar